The rapid pace of technological innovation has brought about numerous benefits, but it has also led to a concerning surge in electronic waste, or e-waste. As our reliance on electronic devices continues to grow, the challenges associated with managing e-waste have become increasingly apparent. This article explores the complexities of e-waste management, examining the challenges faced and proposing potential solutions to address this pressing environmental issue.
**1. The Escalating Issue of E-Waste
Electronic devices, ranging from smartphones and laptops to refrigerators and televisions, have a finite lifespan. The disposal of these devices contributes to the growing global challenge of e-waste. According to the Global E-Waste Monitor, approximately 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste were generated worldwide in 2019, with only 17.4% of it being officially documented as properly collected and recycled.
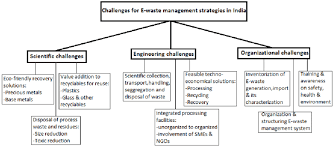
**2. Challenges in E-Waste Management
2.1 Lack of Proper Collection Systems
One of the primary challenges in e-waste management is the inadequate infrastructure for collecting electronic devices at the end of their life cycle. Many regions lack efficient systems for gathering e-waste, leading to improper disposal methods such as landfilling or incineration.
2.2 Informal Recycling Practices
In some parts of the world, e-waste is processed through informal recycling practices. While these operations may recover certain valuable materials, they often involve unsafe and environmentally harmful methods, exposing workers to hazardous substances.
2.3 Complex Composition and Hazardous Materials
Electronic devices are composed of a complex array of materials, including metals, plastics, and hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and brominated flame retardants. Disposing of these devices without proper treatment poses risks to both human health and the environment.
2.4 Global Trade of E-Waste
The global trade of e-waste, often to developing countries, exacerbates the problem. While intended for recycling, a significant portion ends up being mishandled, leading to environmental pollution and health hazards in receiving countries.
2.5 Consumer Awareness and Behavior
A lack of awareness among consumers regarding proper e-waste disposal and recycling options contributes to the challenge. Many individuals discard electronic devices in regular waste bins, unaware of the potential environmental impact.
**3. Potential Solutions to E-Waste Management
3.1 Strengthening Collection Infrastructure
Addressing the issue of inadequate collection requires the establishment and improvement of collection systems. Governments and municipalities should invest in accessible and convenient e-waste collection points, making it easy for individuals to responsibly dispose of their electronic devices.
3.2 Promoting Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Implementing Extended Producer Responsibility programs places the onus on manufacturers to manage the end-of-life disposal of their products. This encourages companies to design products with easier recyclability in mind and take responsibility for the collection and recycling of devices.
3.3 Investing in Safe Recycling Technologies
Investing in safe and efficient recycling technologies is crucial. Advanced recycling methods can extract valuable materials from electronic devices while minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, promoting research into eco-friendly alternatives for electronic components can reduce reliance on hazardous materials.
3.4 Educating and Raising Awareness
Increasing public awareness about the importance of proper e-waste disposal is essential. Educational campaigns can inform consumers about the potential environmental and health risks associated with improper disposal and encourage responsible recycling practices.
3.5 International Cooperation and Regulation
Addressing the global trade of e-waste requires international cooperation. Implementing and enforcing regulations on the export and import of e-waste can help prevent the illegal dumping of electronic devices in developing countries.
**4. Conclusion
E-waste management is a critical environmental challenge that demands immediate attention and concerted efforts. The escalating volumes of electronic devices being discarded worldwide necessitate comprehensive strategies that span collection, recycling, and responsible consumer behavior. By investing in infrastructure, promoting producer responsibility, advancing recycling technologies, and raising public awareness, we can work towards mitigating the impact of e-waste on the environment and building a more sustainable future. It is essential for individuals, industries, and governments to collaborate in finding and implementing effective solutions to ensure the responsible management of electronic waste for the well-being of our planet and future generations.